Engineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition PDF Solutions unlocks the secrets of structural analysis, empowering engineers with the knowledge to design and optimize structures that withstand the forces of nature. This comprehensive guidebook provides step-by-step solutions to complex statics problems, enabling students and professionals to master the fundamental principles of equilibrium, internal forces, and structural behavior.
Delve into the intricacies of statics, exploring the concepts of forces, moments, and equilibrium. Analyze the internal forces within structures, including axial forces, shear forces, and bending moments. Discover the significance of centroids and moments of inertia in structural design, and delve into the practical applications of friction in engineering systems.
Overview of Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Engineering mechanics is a branch of physics that deals with the analysis and design of structures subjected to forces. It is a fundamental discipline in engineering and provides the foundation for understanding the behavior of structures under various loading conditions.
Statics, a branch of engineering mechanics, focuses on the analysis of objects at rest or in equilibrium.
Statics plays a crucial role in engineering design and analysis. It enables engineers to predict the forces and moments acting on structures, ensuring their stability and safety. By understanding the principles of statics, engineers can design structures that can withstand external loads and forces, preventing failures and ensuring the integrity of structures.
Scope and Fundamental Concepts of Statics
- Equilibrium: The study of forces and moments acting on objects at rest or in motion.
- Forces: Vectors that represent the interaction between objects, causing changes in motion or deformation.
- Moments: Vectors that represent the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis.
- Equations of equilibrium: Mathematical equations that describe the conditions under which an object is in equilibrium.
Importance of Statics in Analyzing and Designing Structures
- Predicting structural behavior under various loading conditions.
- Ensuring the stability and safety of structures.
- Optimizing structural designs for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
- Preventing structural failures and ensuring public safety.
Equilibrium of Forces and Moments: Engineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition Pdf Solutions
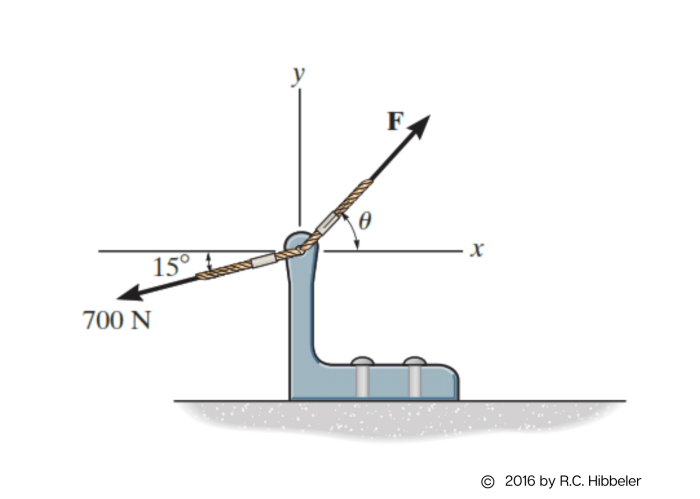
Equilibrium is a state in which the net force and net moment acting on an object are both zero. An object in equilibrium is either at rest or moving with constant velocity.
Types of Forces and Moments
- Point force: A force acting at a single point.
- Distributed force: A force spread over an area or volume.
- Moment: A force that tends to rotate an object about an axis.
Equations of Equilibrium
- For a particle in equilibrium: ΣF x= 0, ΣF y= 0
- For a rigid body in equilibrium: ΣF x= 0, ΣF y= 0, ΣM z= 0
Applications in Solving Engineering Problems
- Analyzing the forces and moments acting on a bridge under traffic load.
- Determining the stability of a retaining wall subjected to earth pressure.
- Calculating the forces in the members of a truss structure.
Structures and Internal Forces
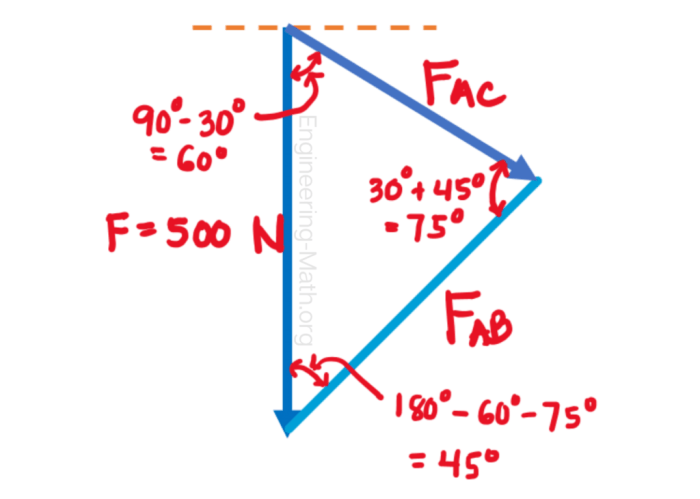
Structures are assemblies of components that are designed to withstand external loads and forces. They can be classified based on their geometry and loading conditions.
Internal Forces
- Axial force: A force that acts along the longitudinal axis of a member.
- Shear force: A force that acts perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of a member.
- Bending moment: A force that tends to bend a member.
Methods for Determining Internal Forces
- Method of sections
- Shear and moment diagrams
Applications in Structural Analysis
- Designing structural members to resist internal forces.
- Predicting the behavior of structures under various loading conditions.
- Optimizing structural designs for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Centroids and Moments of Inertia
The centroid of a shape is the geometric center of the area or volume. The moment of inertia is a measure of the resistance of a shape to bending.
Centroids
- Definition: The point at which the entire area or volume of a shape is assumed to be concentrated.
- Methods for determining centroids: Integration, geometric formulas, experimental methods.
Moments of Inertia
- Definition: A measure of the resistance of a shape to bending.
- Types of moments of inertia: Area moment of inertia, mass moment of inertia.
- Applications: Structural analysis, design of beams and columns.
Friction and Applications

Friction is a force that opposes the relative motion of two surfaces in contact. It is a complex phenomenon that depends on various factors such as the surface roughness, material properties, and normal force.
Types of Friction
- Static friction: Friction that opposes the initiation of motion.
- Kinetic friction: Friction that opposes motion once it has started.
- Rolling friction: Friction that opposes the rolling of one surface on another.
Laws of Friction
- Coulomb’s law of friction: f ≤ μN, where f is the friction force, μ is the coefficient of friction, and N is the normal force.
- Amontons’ laws of friction: The coefficient of friction is independent of the area of contact and the velocity of sliding.
Applications in Engineering Design
- Designing brakes and clutches.
- Analyzing the stability of objects on inclined surfaces.
- Predicting the performance of bearings and other mechanical components.
Applications in Engineering Design

Statics is widely applied in the design and analysis of various engineering structures, including bridges, buildings, and machines.
Bridge Design
- Analyzing the forces and moments acting on a bridge under traffic load.
- Designing the structural members to resist these forces and moments.
- Ensuring the stability and safety of the bridge.
Building Design
- Analyzing the forces and moments acting on a building due to wind, snow, and earthquake loads.
- Designing the structural members to resist these forces and moments.
- Ensuring the stability and safety of the building.
Machine Design, Engineering mechanics statics 14th edition pdf solutions
- Analyzing the forces and moments acting on machine components.
- Designing the components to resist these forces and moments.
- Ensuring the efficiency and reliability of the machine.
Expert Answers
What are the key concepts covered in Engineering Mechanics Statics?
Engineering Mechanics Statics focuses on the analysis of forces and their effects on stationary structures. Key concepts include equilibrium, internal forces, centroids, moments of inertia, and friction.
How can I use Engineering Mechanics Statics 14th Edition PDF Solutions?
This guidebook provides detailed solutions to problems from the 14th edition of Engineering Mechanics Statics textbook. Use it to check your answers, gain insights into problem-solving techniques, and enhance your understanding of the subject matter.
What are the practical applications of Engineering Mechanics Statics?
Engineering Mechanics Statics is essential for designing and analyzing structures such as bridges, buildings, and machines. It helps engineers ensure the safety and stability of these structures under various loading conditions.