How does photosynthesis work label the diagram answer key – With “How Does Photosynthesis Work: Label the Diagram Answer Key” as our guide, we delve into the fascinating world of photosynthesis, a process that sustains life on Earth. This journey will unravel the intricacies of this natural phenomenon, providing a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms, significance, and impact.
Photosynthesis, the process by which plants and other organisms convert light energy into chemical energy, is essential for the survival of our planet. It not only provides the food we eat but also releases oxygen into the atmosphere, making it breathable for all living beings.
Understanding how photosynthesis works is crucial for appreciating its vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of our ecosystem.
Diagram of Photosynthesis: How Does Photosynthesis Work Label The Diagram Answer Key
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The diagram below shows the key structures involved in photosynthesis:
- Chloroplasts: These are the organelles in plant cells that contain chlorophyll, the green pigment that absorbs sunlight.
- Leaves: Leaves are the primary site of photosynthesis in plants. They contain chloroplasts and stomata, which are small pores that allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to exit.
- Stomata: These are small pores on the surface of leaves that allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to exit.
Steps of Photosynthesis
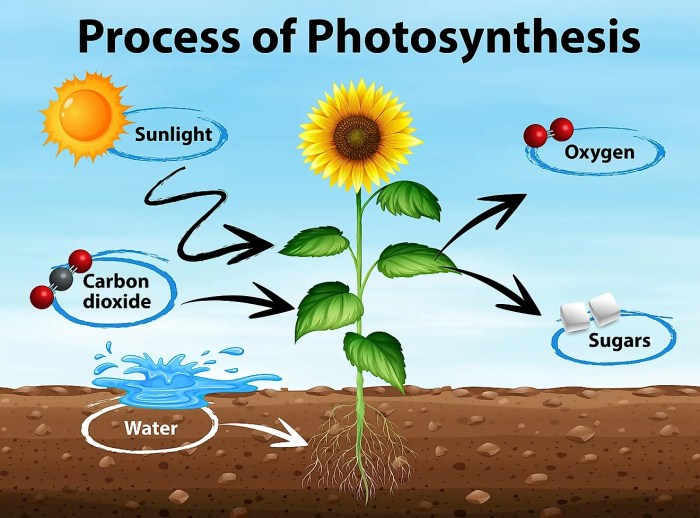
Photosynthesis occurs in two main stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle.
- Light-dependent reactions: These reactions use light energy to convert water into oxygen and generate ATP and NADPH, which are energy-carrier molecules.
- Calvin cycle: This cycle uses the ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
Light-Dependent Reactions
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts. They use light energy to convert water into oxygen and generate ATP and NADPH.
- Photolysis: This is the process by which water is split into oxygen, protons, and electrons.
- Electron transport chain: The electrons generated by photolysis are passed through a series of electron carriers, which generate ATP.
- NADPH: The protons generated by photolysis are used to generate NADPH.
Calvin Cycle, How does photosynthesis work label the diagram answer key
The Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma of chloroplasts. It uses the ATP and NADPH generated in the light-dependent reactions to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
- Carbon fixation: This is the process by which carbon dioxide is incorporated into organic molecules.
- Reduction: This is the process by which carbon dioxide is converted into glucose.
- Regeneration: This is the process by which the ATP and NADPH used in the Calvin cycle are regenerated.
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
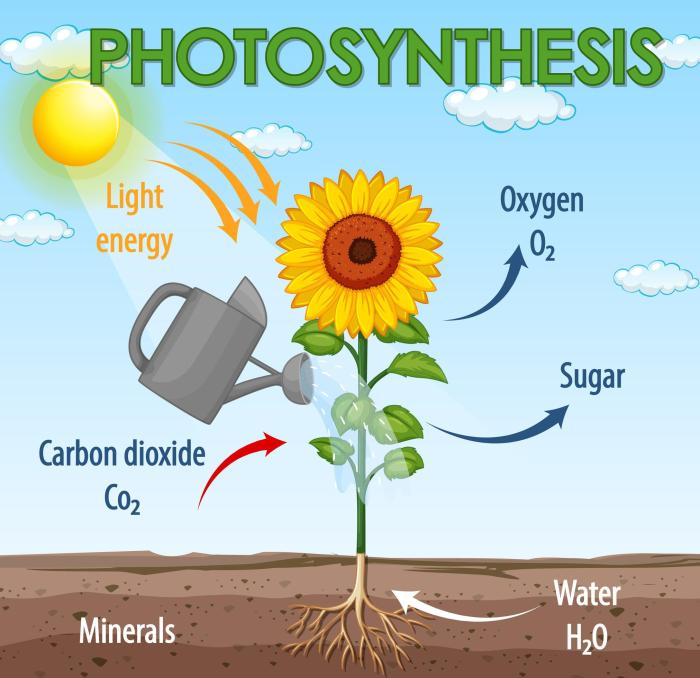
The rate of photosynthesis is affected by a number of factors, including:
- Light intensity: The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing light intensity.
- Temperature: The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing temperature, up to an optimum temperature.
- Carbon dioxide concentration: The rate of photosynthesis increases with increasing carbon dioxide concentration.
Importance of Photosynthesis
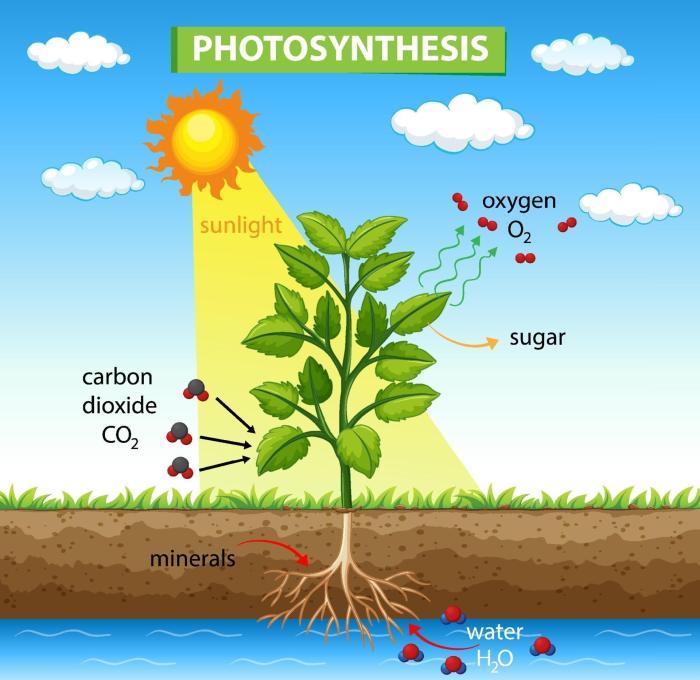
Photosynthesis is essential for life on Earth. It provides the food and oxygen that all animals, including humans, need to survive.
- Food: Photosynthesis is the primary source of food for all animals. Plants use the energy from sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, which is a sugar that can be used for energy.
- Oxygen: Photosynthesis is also the primary source of oxygen for all animals. Plants release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis.
- Climate regulation: Photosynthesis helps to regulate the Earth’s climate by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Carbon sequestration: Photosynthesis helps to sequester carbon from the atmosphere by storing it in plants and soil.
Top FAQs
What is the overall equation for photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Where does photosynthesis take place?
In the chloroplasts of plant cells
What is the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis?
To absorb light energy and convert it into chemical energy
What are the two main stages of photosynthesis?
Light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle
