Sickle cell disease NCLEX questions are an essential resource for nurses seeking to expand their knowledge and enhance their ability to provide optimal care to individuals affected by this debilitating condition. This comprehensive guide delves into the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and nursing care considerations associated with sickle cell disease, empowering nurses with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively navigate the challenges posed by this complex disorder.
Pathophysiology of Sickle Cell Disease
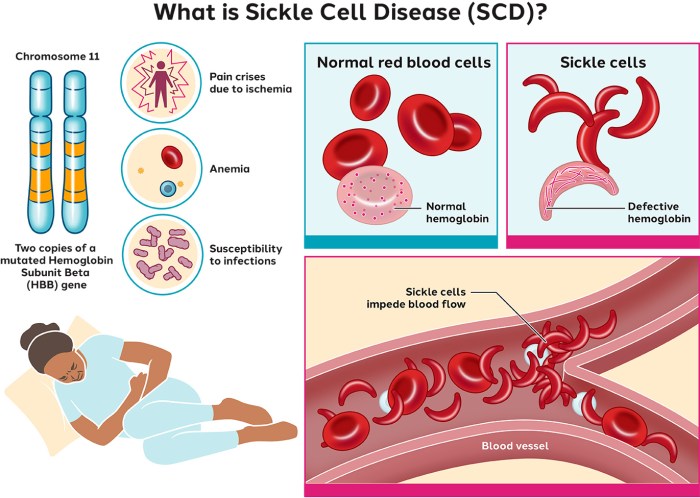
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is a genetic disorder characterized by the production of abnormal hemoglobin (HbS), resulting in the sickling of red blood cells. This abnormality leads to a cascade of pathophysiological events that contribute to the clinical manifestations of SCD.
Genetic Basis
- SCD is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.
- Individuals with SCD inherit two copies of the mutated HbS gene (HbS/HbS).
- Heterozygous individuals (HbA/HbS) are carriers of the disease but typically do not exhibit symptoms.
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms, Sickle cell disease nclex questions
- HbS contains a single amino acid substitution (glutamic acid to valine) at position 6 of the beta-globin chain.
- Under conditions of low oxygen tension, HbS molecules polymerize, causing red blood cells to assume a rigid, sickle shape.
- Sickled red blood cells are less flexible and more prone to hemolysis and vaso-occlusion.
Consequences of Sickling
- Hemolysis:Sickled red blood cells are prematurely destroyed in the spleen and liver, leading to chronic anemia.
- Vaso-occlusion:Sickled red blood cells can obstruct small blood vessels, causing pain crises, tissue ischemia, and organ damage.
- Organ damage:Chronic vaso-occlusion can lead to damage to organs such as the brain, kidneys, lungs, and heart.
Question & Answer Hub: Sickle Cell Disease Nclex Questions
What is the genetic basis of sickle cell disease?
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder caused by a mutation in the beta-globin gene, which leads to the production of abnormal hemoglobin (hemoglobin S).
What are the consequences of sickling?
Sickling of red blood cells can result in hemolysis (destruction of red blood cells), vaso-occlusion (blockage of blood vessels), and organ damage.
What are the acute and chronic complications of sickle cell disease?
Acute complications include pain crises, anemia, stroke, and pulmonary hypertension. Chronic complications can include chronic pain, organ damage, and shortened life expectancy.
What are the principles of comprehensive management for sickle cell disease?
Comprehensive management includes pain management, transfusion therapy, hydroxyurea, and stem cell transplant.
What are the nursing assessment priorities for individuals with sickle cell disease?
Nursing assessment priorities include pain assessment, monitoring for complications, and psychosocial assessment.